Securin Zero-Days
CVE-2020-5504 - SQL Injection with Missing Functional Level Access in phpMyAdmin
Description
A SQL injection (SQLi) refers to an injection attack wherein an attacker can execute malicious SQL statements that control a web application’s database server. Missing functional level access flaws allow attackers to access unauthorized functionality. SQL injection (SQLi) vulnerability was identified with the conjunction of missing function level access in the latest version of the phpMyAdmin database. The vulnerability affects http://localhost/phpmyadmin/server_privileges.php, username.
*Affected Products: phpMyAdmin 4.x versions prior to 4.9.4 are affected, phpMyAdmin 5.x version 5.0.0
Proof of Concept (POC):
The following vulnerability was tested on phpMyAdmin version 5.0.
Issue: SQL Injection with missing functional level access:
1. Log in to the phpMyAdmin GUI
2. Installed PhpMyAdmin (Version 5.0)
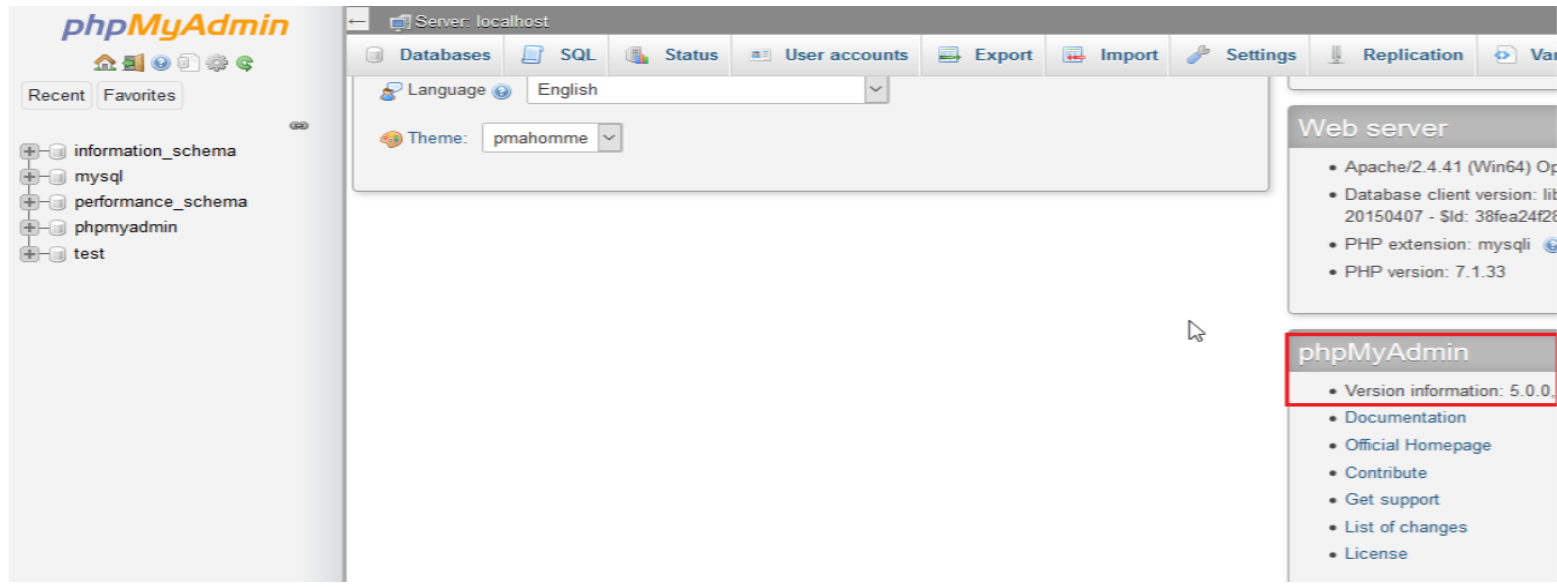
Figure 01: phpMyAdmin Installed Version 5.0.0
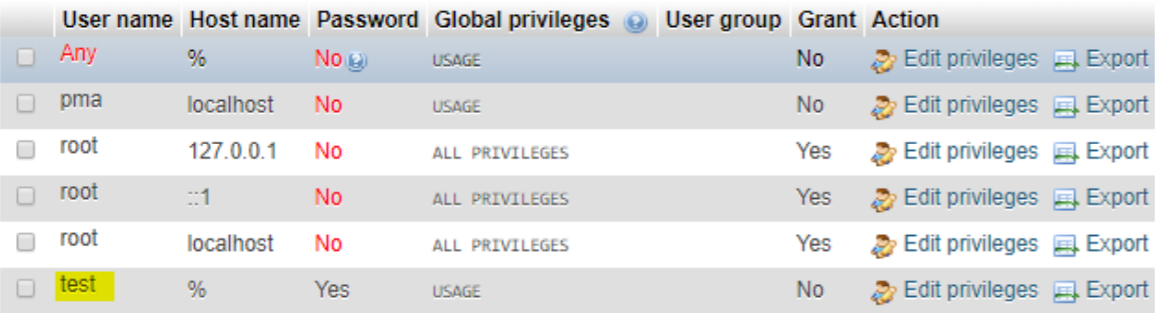
Figure 02: List of user accounts and privileges in the database.
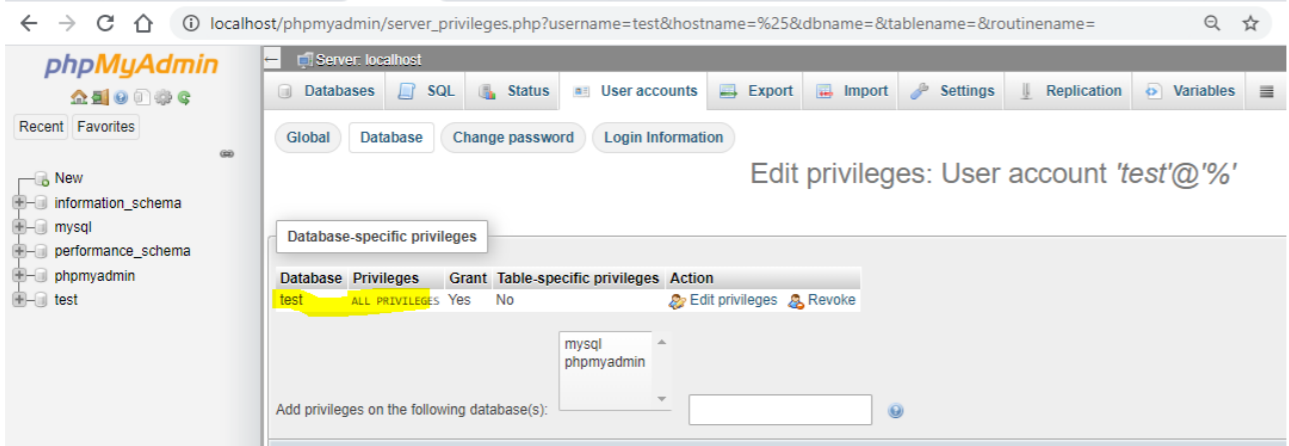
Figure 03: Test user doesn’t have global privileges just for information.
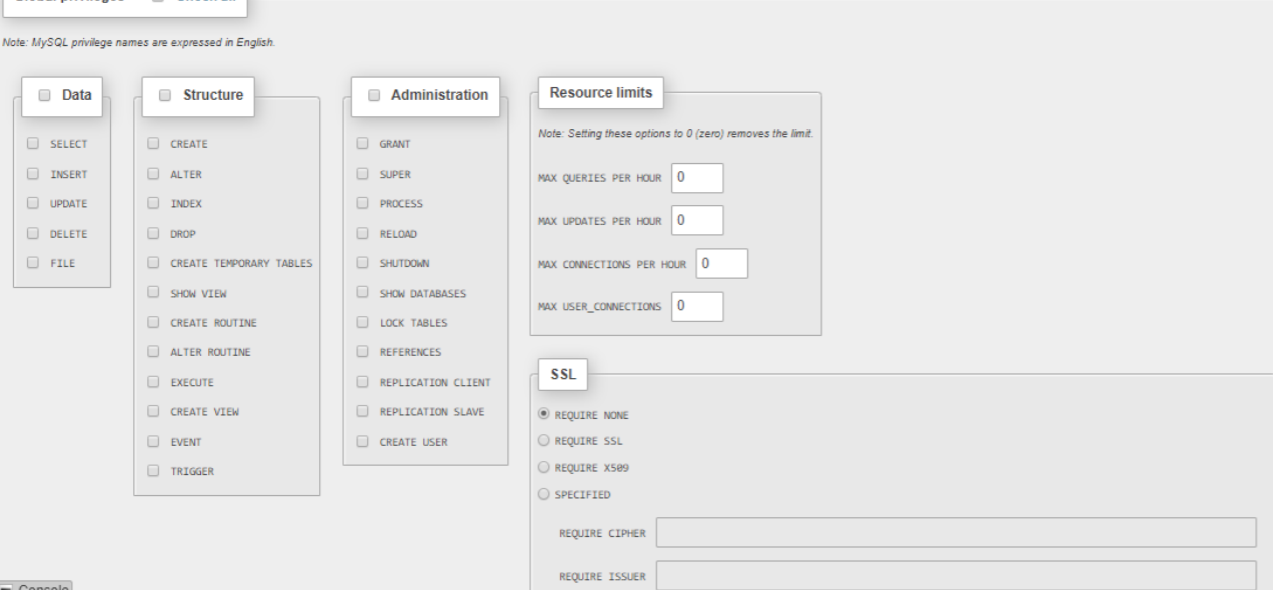
Figure 04: “Test” user has all privilege to test the database only.
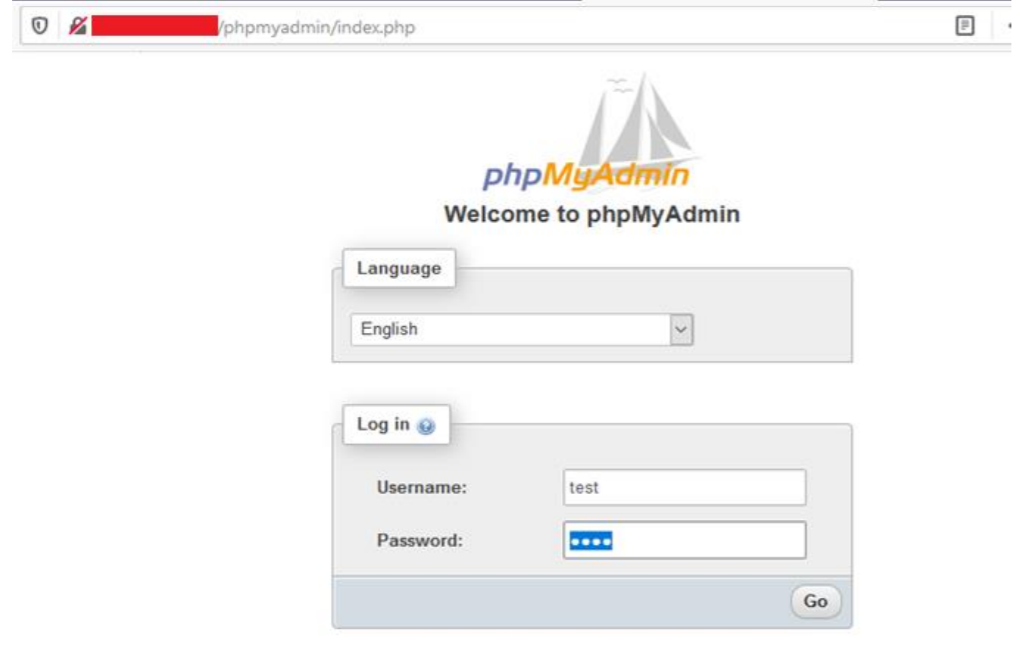
Figure 05: Log in to phpMyAdmin with “test” user credentials.
Now, enable an http-based proxy on the browser to intercept the traffic to the server.
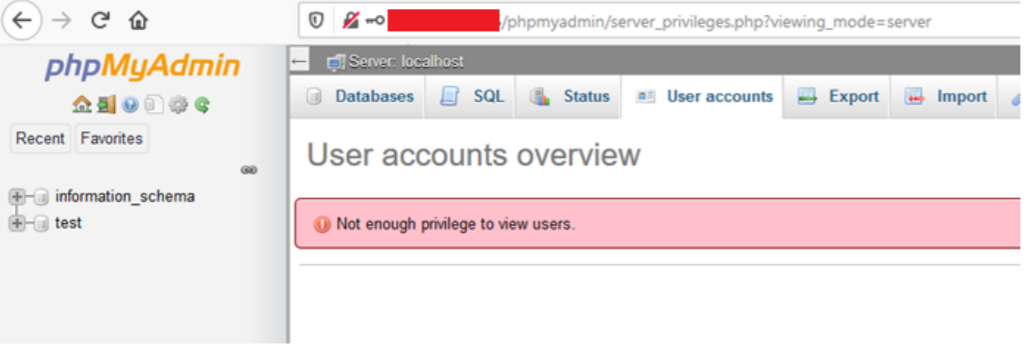
Figure 06: “Test” users don’t have enough privilege to view users and other databases.
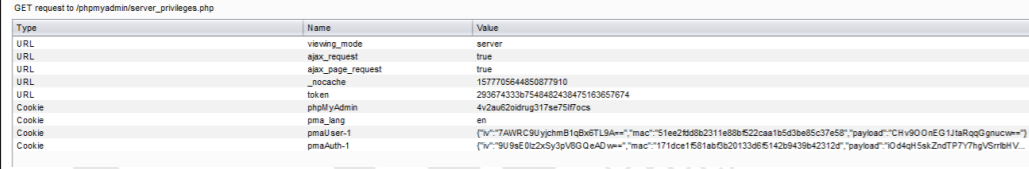
Figure 07: The intercepted ajax call in the proxy is related to the user accounts page.
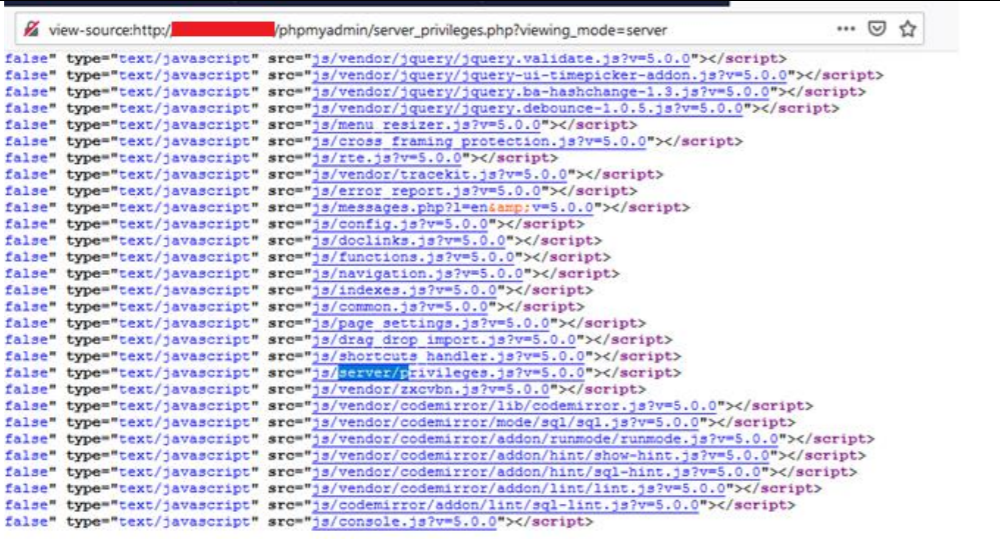
Figure 08: JavaScript file which related to server_privileges.php page Ajax calls.
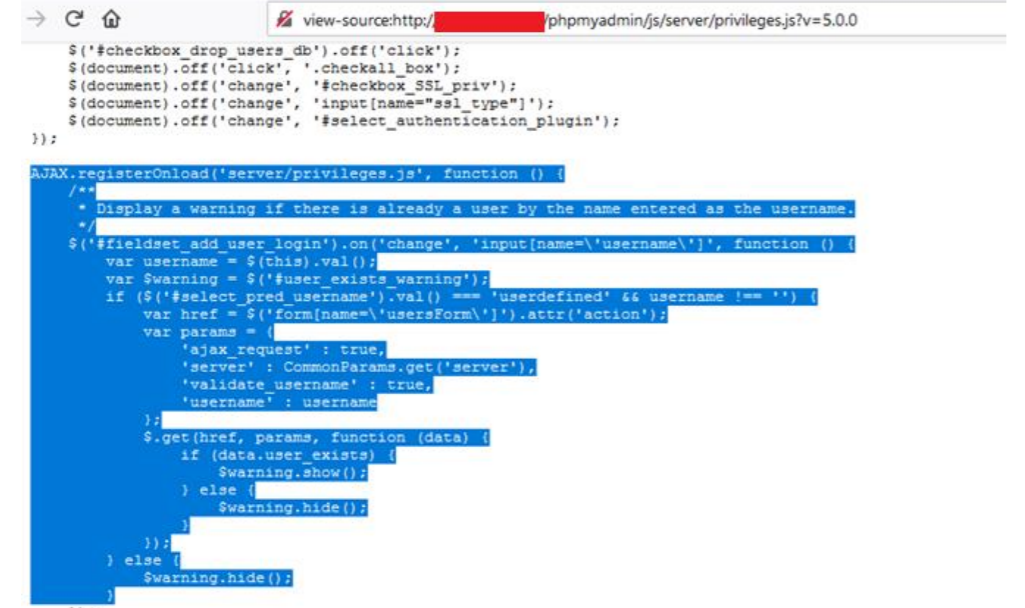
JavaScript code, which is responsible for checking the existence of the username in the database.
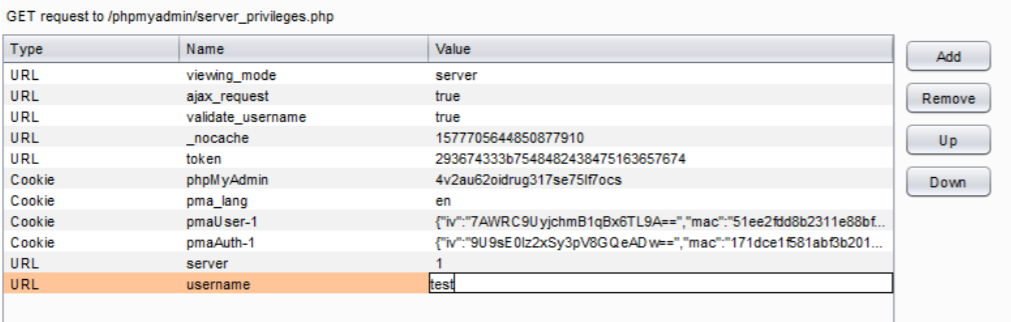
modified Ajax call which was intercepted in Burp with the required details to make validate_username
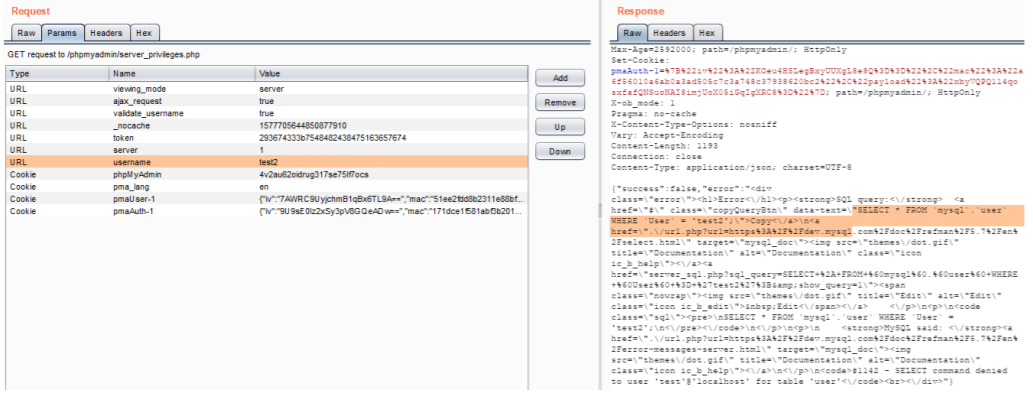
As per the privileges, the user shouldn’t be able to access this ajax call. But the server is giving a SQL error in the response. The response for the Ajax call confirms that the request is vulnerable to Missing Functional Level Access.
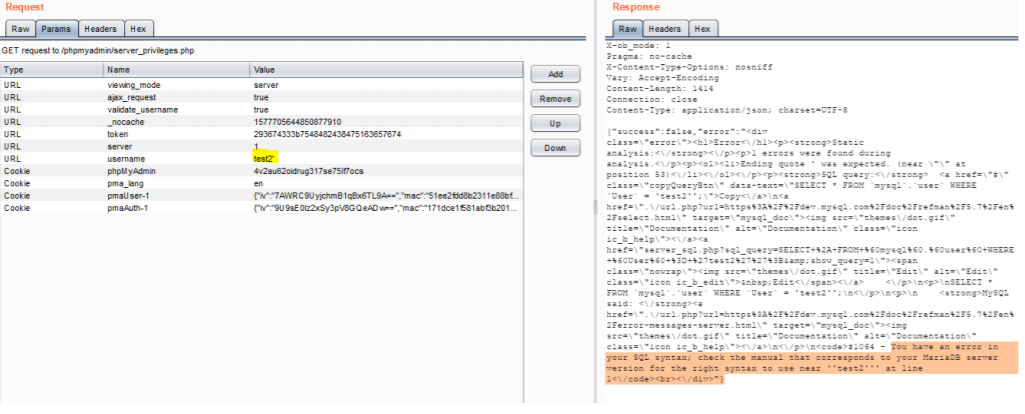
An unauthorized (test) user was able to control the SQL statement, which is responsible for validating username.
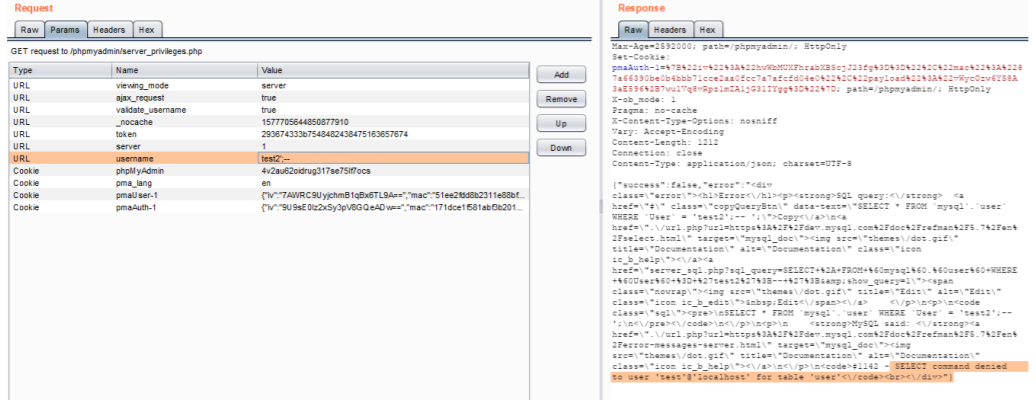
Difference in the responses of the previous request and the current request confirms the username field is vulnerable to SQL injection.
Impact
An authenticated user who has the privileges to one database at least can retrieve the contents of the databases in the MySQL DBMS server. Under the right circumstances, SQLi can also be used by an attacker to execute OS commands, which may then be used to escalate an attack even further.
Remediations
Download the following patches advised as per the vendor.
For 4.8, 4.9 versions: upgrade to version 4.9.4 or newer, 5.x: upgrade to version 5.0.1, or newer, or apply the patch below.
Older versions: https://gist.github.com/ibennetch/4c1b701f4b766e4dd5556e8e26200b6b
Timeline